Ad Rank plays a crucial role in determining where your ads appear in Google search results. Whether you are running a Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaign for a small business or managing large-scale Google Ads, understanding Ad Rank is essential. Without a strong Ad Rank, your ads may not get the visibility they deserve, leading to higher costs and lower returns on investment.
In this comprehensive guide, we will break down what Ad Rank is, how it is determined, how it is calculated, and actionable tips to improve it without necessarily increasing your bids. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to maximize your Google Ads performance while keeping costs under control.
What is Ad Rank?

Ad Rank is a crucial metric in Google Ads that determines the position of your ad on the search engine results page (SERP). It is not solely based on the bid amount but rather a combination of several factors such as ad quality, relevance, expected click-through rate (CTR), and landing page experience. Google uses Ad Rank to ensure that the most relevant ads appear in prime positions rather than just the highest bidders.
At its core, Ad Rank helps Google maintain the integrity of its advertising platform by ensuring users see ads that are both relevant and valuable. This means that even advertisers with lower bids can secure higher ad positions if they offer high-quality ads with better relevance and user experience.
Key Aspects of Ad Rank:
- Determines Ad Placement: The higher your Ad Rank, the better your ad position in search results.
- Influences Cost-Per-Click (CPC): Advertisers with a higher Ad Rank often pay less per click compared to those with lower ranks.
- Enhances User Experience: Google rewards high-quality, relevant ads with better placement to improve the user experience.
- Balances Competition: Ensures that small businesses with well-optimized ads can compete with larger advertisers.
Ad Rank is recalculated every time a search query is made, meaning that ad positions can change dynamically depending on real-time factors such as competitor bids, search context, and user behavior.
How Ad Rank is Determined
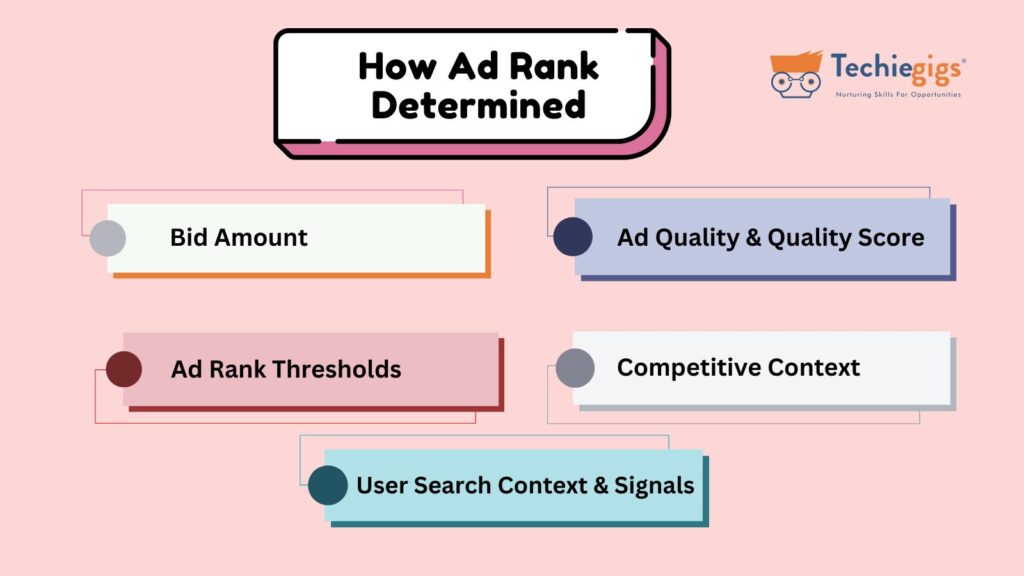
Google Ads uses multiple factors to calculate Ad Rank. Understanding these factors can help you optimize your ad performance effectively.
1. Bid Amount
Your bid is the maximum amount you are willing to pay per click. However, the highest bid does not always win the top position. Google considers multiple elements alongside the bid, ensuring that relevance and quality matter as much as the financial investment.
2. Ad Quality & Quality Score
Quality Score is a major component of Ad Rank. It consists of three elements:
- Expected Click-Through Rate (CTR): The likelihood of users clicking your ad, based on past performance and search relevance.
- Ad Relevance: How closely your ad matches user intent and keyword searches.
- Landing Page Experience: The relevance and usability of your landing page, including load speed, content alignment, and mobile responsiveness.
A higher Quality Score leads to a better Ad Rank, even with a lower bid.
3. Ad Rank Thresholds
Google sets minimum Ad Rank thresholds that your ad must meet to be displayed. These thresholds are influenced by factors such as:
- The search query’s commercial intent
- The industry and competition level
- Ad format and extensions used
- User device and location
Even if you bid high, your ad may not appear if it does not meet the required quality standards.
4. Competitive Context
Your Ad Rank is also influenced by the competition. Google Ads functions on a real-time auction system, meaning that the number and quality of competing ads affect your placement. If competitors have higher Ad Ranks, you may need to optimize your Quality Score, bid strategy, or ad relevance to outperform them.
5. User Search Context & Signals
Google considers additional user signals, such as:
- Location: Ads may be prioritized based on geographic relevance.
- Device Type: Mobile vs. desktop ads may perform differently.
- Search Intent: Google evaluates whether a search is informational, transactional, or navigational.
- Time of Search: The effectiveness of ads may fluctuate based on the time of day, week, or season.
These factors contribute to the real-time auction where Ad Rank is determined, ensuring that the most relevant ads reach the right audience at the right time.
How Ad Rank is Calculated

Ad Rank is calculated using the following formula:
Here’s a simple example:
- Advertiser A: Bid = $2, Quality Score = 8 → Ad Rank = 16
- Advertiser B: Bid = $3, Quality Score = 5 → Ad Rank = 15
Even though Advertiser A has a lower bid, their higher Quality Score gives them a better Ad Rank, meaning they secure a higher ad position.
Ad Rank in Search Ads vs. Display Ads
Ad Rank calculations differ slightly for Google Display Network (GDN) compared to search ads. For Display Ads, engagement metrics such as viewability and audience targeting play a larger role in determining Ad Rank.
How to Improve Your Ad Rank Without Increasing Bids
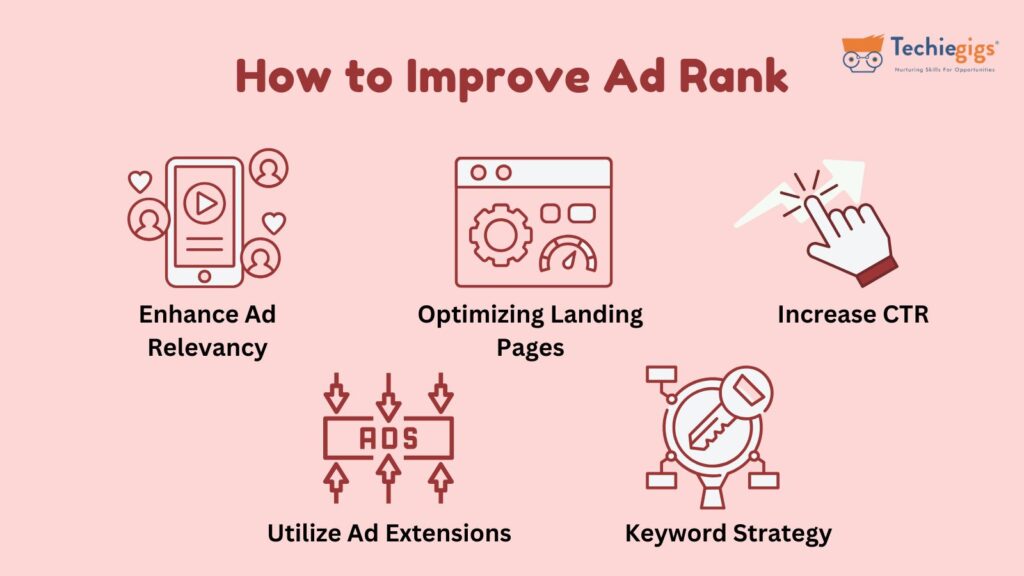
Boosting your Ad Rank does not always require increasing your bid. Below are some proven strategies to enhance your Ad Rank effectively.
1. Enhance Ad Relevance
Google prioritizes ads that closely match the user’s search intent. Use highly relevant keywords in your ad copy, headlines, and descriptions. Ensure that your messaging aligns with the search query.
2. Optimize Landing Pages
A poorly optimized landing page can lower your Ad Rank. Make sure your landing page:
- Loads quickly (under 3 seconds)
- Is mobile-friendly
- Matches the ad’s message
- Includes clear CTAs (Call-To-Actions)
3. Increase Expected CTR
Higher CTR means better Ad Rank. Improve CTR by:
- Writing compelling headlines
- Using emotional triggers in ad copy
- Implementing responsive search ads
4. Utilize Ad Extensions
Google rewards ads that provide more information. Use the following extensions to improve your Ad Rank:
- Sitelinks – Additional links to relevant pages
- Callouts – Highlight offers and benefits
- Structured Snippets – Provide more details about your services
- Call Extensions – Encourage direct customer contact
5. Optimize Your Keyword Strategy
Using the right keywords impacts Ad Rank. Consider:
- Long-tail keywords – Lower competition and higher conversion rates
- Negative keywords – Prevent showing ads for irrelevant searches
- Match types – Use a mix of broad match, phrase match, and exact match keywords
Conclusion
Understanding and optimizing Ad Rank is critical to running cost-effective and high-performing Google Ads campaigns. Rather than just increasing your bid, focus on improving ad quality, relevance, and landing page experience. By leveraging Ad Rank factors wisely, you can achieve better ad placements while keeping advertising costs manageable.
Would you like to see how your current Ad Rank strategy is performing? Start by conducting a Google Ads audit today and optimize your campaigns for better results!



